NodeGopher
is a Node Graph Grafana/Prometheus helper
Its purpose in life is to help you create NodeGraphs like network or application topology, arranging nodes and edges, and dynamically query prometheus to add stat to graph items.
It support instant and range queries. Range query results will be averaged to get one metric.
Technically, it is an API which builds json nodegraph structure to be exposed to grafana. To enrich this structure with metrics, nodegopher query a prometheus instance.
It gets time range values from Grafana, so it can relay them to prometheus if you want to average values from a time range.
Configuration
see config.yaml.sample
Grafana datasource
Successfully tested with yesoreyeram-infinity-datasource datasource
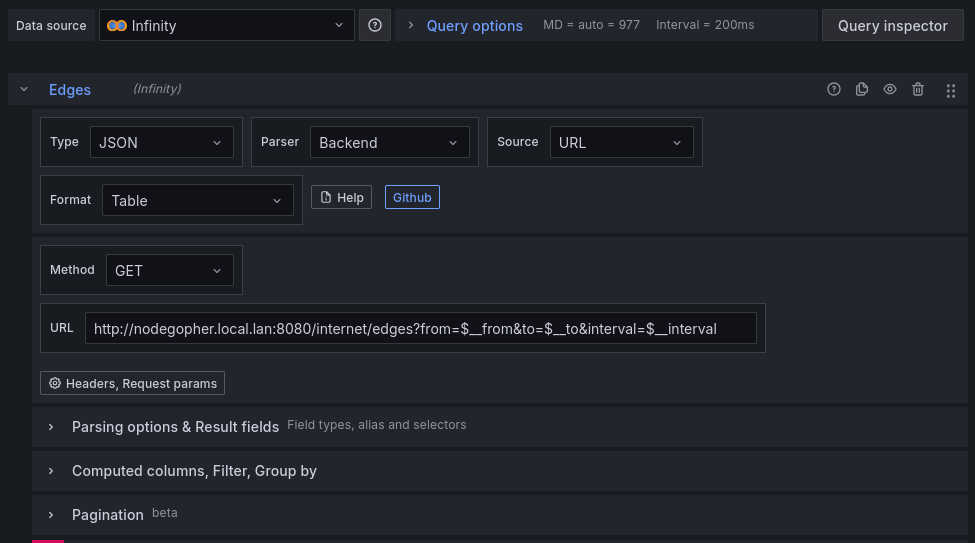
Create an infinity query, name it "Edges". Type "JSON", Parser "Backend", Source "URL", Format "Table", Method "GET"
URL: "http://my-nodegopher-host:8080/graph1/edges?from=$__from&to=$__to&interval=$__interval"
Create a second infinity query named "Nodes", same config,
URL: "http://my-nodegopher-host:8080/graph1/nodes?from=$__from&to=$__to&interval=$__interval"
switch to visualization type "NodeGraph", and voila
Instance management
Reload configuration
You can reload configuration file when the API is running, with either sending a signal, or make a POST request.
Using SIGHUP :
kill -HUP `pgrep nodegopher`
Sending POST on /reload :
curl -XPOST http://my-nodegopher-host:8080/reload
{"message":"configuration successfully reloaded"}
Reloading a badly formated configuration will produce an error and keep the old configuration running.
% curl -XPOST 127.1:8080/reload
{"error":"Unable to load new configuration, keeping old one. See logs."}